Introduction
Sexual health is an important aspect of overall well-being, and it is crucial to have proper education and awareness about sexually transmitted infections (STIs). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into one particular STI - syphilis. We will provide a detailed overview of its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods. Our goal is to equip individuals with the knowledge they need to protect themselves and their partners.
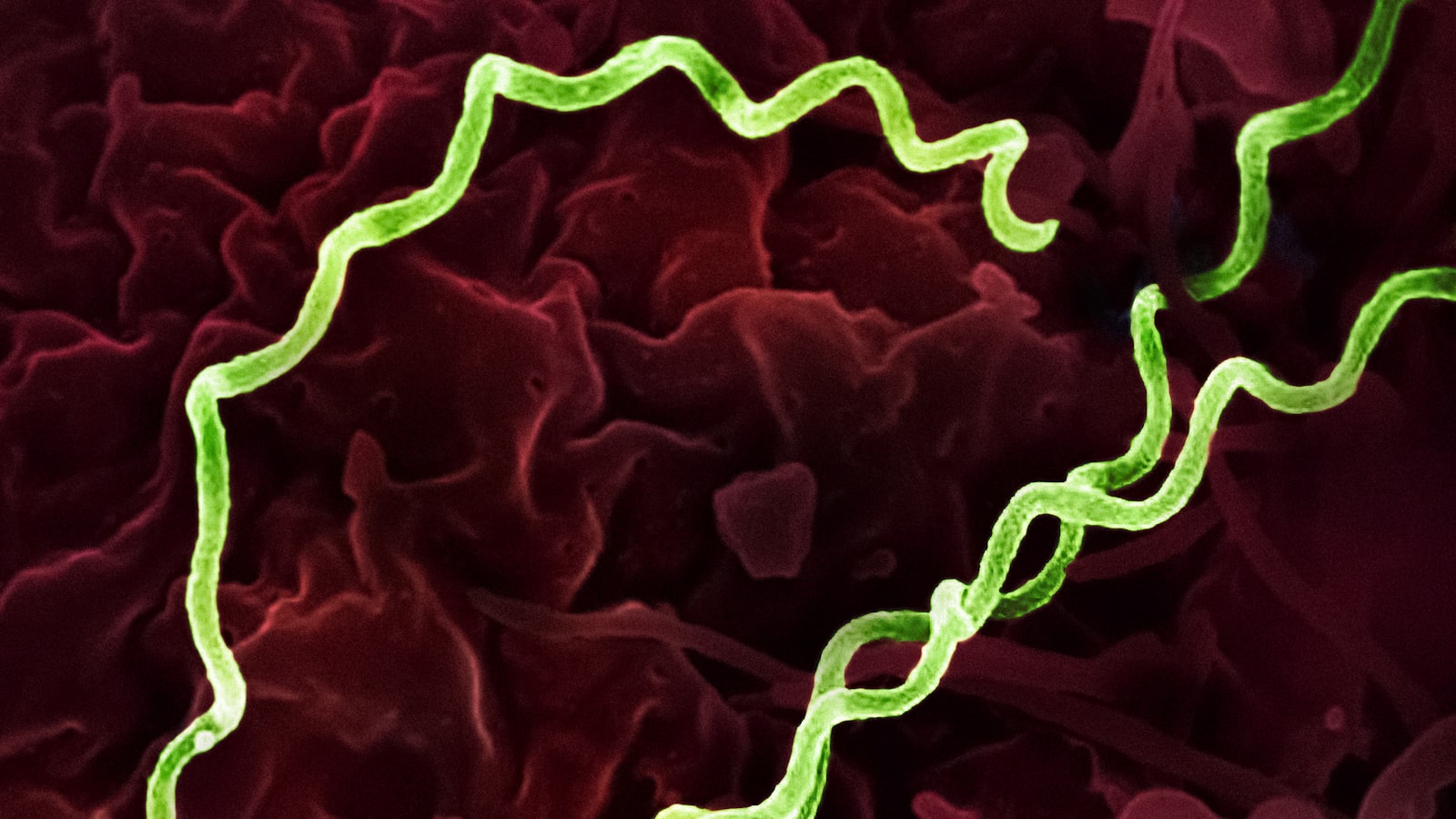
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a highly contagious bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Additionally, it can be transmitted from an infected mother to her unborn child during pregnancy. Syphilis progresses in stages, with each stage presenting different symptoms and complications.
Symptoms
The symptoms of syphilis vary depending on the stage of infection. In the primary stage, a painless sore called a chancre appears at the site of infection, usually in the genital area, anus, or mouth. If left untreated, the infection progresses to the secondary stage, characterized by a rash, fever, sore throat, and swollen glands. The latent stage follows, during which no symptoms are present. Finally, in the tertiary stage, syphilis can cause severe damage to the internal organs, nervous system, and brain.
Diagnosis
To diagnose syphilis, healthcare professionals may conduct a variety of tests, including blood tests, physical examinations, and analysis of fluid from a chancre or rash. Early detection is crucial to prevent further transmission and complications.
Treatment
The treatment of syphilis typically involves the administration of antibiotics, primarily penicillin. The type and duration of treatment depend on the stage and severity of the infection. It is essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor the progress and ensure effective treatment.
Prevention
Prevention plays a vital role in combating syphilis. Practicing safe sex, including the consistent use of condoms, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Regular testing for STIs is a crucial aspect of maintaining sexual health and preventing the spread of infections. Additionally, it is essential for pregnant individuals to receive prenatal care and be tested for syphilis to prevent transmission to the unborn child.
Conclusion
Syphilis is a serious STI that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Educating ourselves and others about syphilis and other STIs is essential for promoting sexual health and preventing their spread. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods of syphilis, we can take proactive steps towards a healthier and safer sexual future.
#sexualhealth #STIs #syphilisawareness #safepractices #preventionsmatters